Gilets Jaunes: Is the Energy Transition Possible while still Reducing Inequality?
by Evens Salies
The gilets jaunes (“yellow vests”)[1] movement offers a striking opportunity to ask whether the Sustainable Development Goals for achieving an energy transition and reducing income inequalities are fundamentally incompatible. Our answer is no! Both objectives must and can be met simultaneously: the political acceptability of environmental policies, such as carbon pricing and subsidies for green technologies, crucially hinges upon their distributional effects. While the concept of the ‘just (fair) transition to low-carbon energy’ for workers has figured in the climate debate at the annual COP meetings[2], the issue of how to spread the cost burden of this transition among end-consumers remains somewhat out of the frame. Clear guidelines on the design of energy transition policies that have adverse effects on low-income households are still needed in France.[3]
To give some context, the yellow vests movement began in November 2018 in response to a programmed rise in carbon taxes, which coincided with a 25% increase in car fuel prices (see the figure below) and followed previous hikes in oil prices and fuel taxes. The government ended up cancelling this measure in December in response to street pressure.
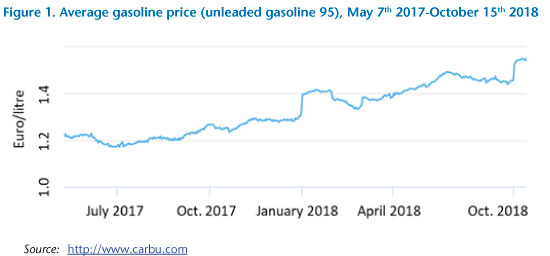
The higher carbon tax was part of a package previously issued under the Hollande presidency, which consisted of two main measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the automobile sector. The first measure consisted in increasing the taxes on gasoline and diesel fuels by nearly 5 and 8 cents (€) per litre (excl. value-added tax), respectively. That is an approximate increase of between 3% and 5% on the final price paid at the pump, which currently averages €1.40/litre. The so-called TICPE (domestic tax on the consumption of oil products) is the main tax on car fuels. The 2015 Finance Bill split TICPE into two components, an ‘energy’ component (new TICPE) and a ‘carbon tax’ component, the future values of which are already planned until 2022 based on a trajectory determined by the Quinet commission.[4] On top of the TICPE, a value-added tax of 20% is applied so that two-thirds of car fuel prices are now made up of taxes.
Second, the policy package envisaged a flat subsidy of up to €2,500 on the purchase of an electric vehicle (“EV”) for people who scrap their old car. The French government went in the right direction by reforming this subsidy following protests earlier in December last year; it is now twice as much for the most vulnerable households. From a welfare economics perspective, there are clear reasons to oppose the government’s original policy package.
Despite the existence of an ‘energy cheque’ for domestic gas and electricity consumers, and a bonus-malus scheme on the purchase of new cars depending on their CO2 emission rate, car fuel taxes disproportionately affect the poor. There are also clear differences between small and large cities, as shown by Paul Malliet, who examined the carbon tax equity puzzle using the 2011 Family Expenditure Survey. Taxes on fuels are regressive, as is car fuel pricing. Like other necessity goods, their share in the budget is higher for poorer households. Using the previous version of the Family survey, more precisely that for 2006, we find results that are qualitatively similar to Malliet’s: the income share of car fuel expenditure is 9.2% for households with income in the 0-20% bracket and 3.2% for those in the 80-100% bracket. In the case of diesel fuel, the incidence of a 5% price increase is roughly twice as much for the bottom 20% of households as for the median household; indeed, it amounts to approximately 0.4% of the annual income of the former.
In addition, financial constraints (access to capital and loans) make it more difficult for poorer households to switch to low-emission vehicles, even subsidized ones, if the subsidy is insufficient to help consumers reach a certain threshold. This is reflected in the low estimated short-run value for the percentage decrease in car fuel consumption, -0.2%, in response to a 1% increase in fuel prices.[5] Furthermore, the environment is likely an inferior good for poorer consumers, who must first satisfy basic needs, such as food, housing and health care. The degree to which consumers have patience to wait the implications of a policy effect is correlated with income; thus, policies that have long-term effects receive less support from poorer strata than those that have immediate effects.
However, one could argue that a 0.4% income loss on average hardly justifies such strong opposition, keeping in mind the little-known fact that France’s after-tax redistribution is one of the highest in the world, and noting that harsh socio-economic conditions already existed upon implementation of the package. These conditions are illustrated by recent research connecting the rise of populism to the several adverse shocks negatively affecting less skilled and less wealthy households alike, notably automation and globalization, while dramatically increasing incomes at the top end of the distribution (Autor et al., 2016; Colantone and Stanig, 2018).[6]
These triggers have been amplified by sociological factors, including the need to belong to a community and be visible and the loss of cultural identity in disadvantaged areas. The distinction between rural (peripheral) and urban living areas, although broad, is interesting here, for the yellow vests movement emerged from within peripheral cities that serve predominantly rural hinterlands. Métropolisation has cut French society in two.[7] Places that globalization has transformed into dynamic urban areas and la France périphérique, where households live far from public and transportation services, spend more on fuel while earning less. Consequently, the incidence of an increase in energy taxes, ceteris paribus, is more effective and harsher for households in these peripheral areas, keeping in mind that car fuel expenditure is 4% higher for the bottom 20% households in rural areas than for urban ones, whereas their monthly income is 3% less.
The question is thus: would it have it been possible to make the package fairer? Our answer is yes, and there are examples to guide a much-needed revision. California implemented a progressive subsidy targeting disadvantaged areas and low- to middle-income households. The large positive impact of such a policy suggests that progressive subsidies can be perceived by individuals as fairer and be more effective than flat ones in terms of creating a mass market for EVs.[8] Indeed, wealthier households are likely to buy an EV even in the absence of a subsidy or in response to steady increases in gasoline prices.[9]
The benefits of progressive subsidies associated with greener cars can be magnified by targeted industrial policies favouring local producers and thus potentially creating jobs in the EU. Policymakers can also envisage clauses for local input content. Another key element is the timing of the subsidy. To enhance the local benefits, a gradual increase of the subsidy over time would likely allow the European automotive industry to have enough time to make investments to adapt to the new regulation, akin to the euro 6 emission standards policy, which gives an appropriate lead time to the industry for introducing technical developments.
We do not want to exaggerate our claims. There is a major obstacle to EV adoption, namely ‘range anxiety’, or the idea that consumers are sensitive to the limited range of an EV (e.g., the stressful situation of the battery running low and the need to drive a longer distance than the EV is usually capable of). This problem is well documented in the 2019 paper by Noel, L. et al., “Fear and loathing of electric vehicles: The reactionary rhetoric of range anxiety,” Energy Research & Social Science, Vol. 48, pp. 96-107. Furthermore, EVs are just one part of the solution; investment in public transportation and urban management are equally important ways to tackle the energy transition while still reducing inequality.
To conclude, we argue that the much-needed political debate ignited by the yellow vests could be considered a unique opportunity for the ruling parties in EU countries to combine the various energy ‘transitions’ with job creation and an increase in perceived or even actual fairness and social security in la France périphérique. Imposing a clause of local-content seems a politically feasible option to grasp the full benefits of a big subsidy push for EVs and other investments in low-carbon transportation infrastructures. The question of how to account for differences between geographical areas when implementing the energy transition is of much importance. France’s current Great National Debate on constitutional issues, taxation and the country’s transition to a low-carbon economy will perhaps offer a step in addressing those issues as well as the main question of who should be in the front line to pay for this energy transition.
Acknowledgments: I would like to thank Francesco Vona for having initiated this small project. I am also grateful to the editor and Paul Malliet who reviewed it, as well as Adam Cutforth, Bodo Steiner and Sarah Guillou for their suggestions for improvements. Any remaining errors are the author’s.
[1] Symbolically linked to the plight of the motorist and commuter, since it is compulsory to have such a yellow vest in every vehicle.
[2] See Vona, F. (forthcoming), “Job losses and the political acceptability of climate policies: why the job killing argument is so persistent and how to overturn it”, Climate Policy.
[3] See Mehling, M., 2018. “Emmanuel Macron’s carbon tax sparked gilets jaunes protests, but popular climate policy is possible”, The Conversation, December 10th.
[4] Based on figures made available by the French Ministry of Ecology, the carbon tax on gasoline was supposed to increase by 2.4 cents (€) in 2019, while that on diesel was supposed to increase by 2.7 cents. The higher increase in the tax on diesel reflects the recent government decision to harmonize the overall taxation of diesel fuel and gasoline as an incentive to reduce consumers’ purchasing of diesel cars because of environmental pressure, perhaps also related to the Volkswagen scandal.
[5] Long-run responses are generally of a higher magnitude. See Collet, R., de Lapparent, M., Hivert, L., 2015, “Are French households car-use addicts? A microeconomic perspective,” in the Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Economics, Vol. 54, pp. 86-94, for a recent study on car fuel elasticities.
[6] Autor, D., Dorn, D., Hanson, G., Majlesi, K., 2016. “Importing political polarization? The electoral consequences of rising trade exposure.” NBER Working Paper No. 22637, September; and, Colantone, I., Stanig, P., 2017. “The trade origins of economic nationalism: Import competition and voting behavior in Western Europe.” American Journal of Political Science, Vol. 62, pp. 936-953.
[7] See Caldwell, C., 2017. “The French fracture.” New Statesman, pp. 30-35. Some writers suggest a further triggering event, in 2013 when Bonnets rouges (“red caps”) protesters forced François Hollande’s government to back away from levying a ‘carbon tax’ on heavy trucks, revealing French drivers’ resistance to environmentally-related taxes
[8] Muehlegger, E., Rapson, D., 2018. “Subsidizing mass adoption of electric vehicles: quasi-experimental evidence from California.” NBER Working Paper No. 25359, December.
[9] An even more ambitious plan would be to make progressive subsides to EVs a pan-European flagship policy to fight climate change, by financing it with a very small EU tax on wealth whose budget will be entirely devoted to greening the automotive industry.