Unemployment: an ambiguous fall, but an unambiguous rise in long-term jobless
Analysis and Forecasting Department (France team)
The unemployment figures for the month of January 2016 published by France’s Pôle Emploi job centre show a fall of 27,900 in the number of job seekers who are not working (category A), which follows an increase recorded in the month of December (+15,800). While this fall might seem encouraging (a decline of this magnitude has not been seen since 2007), it must be qualified. First, recent changes in administrative practices made by Pôle Emploi [1] have resulted in an abnormal increase in exits from the jobless rolls due to failures to update (239,000, against a monthly average of 207,000 in 2015). Second, the high volatility of the monthly figures in recent months is a sign of a labour market in which job creation is insufficient to reduce unemployment on a sustainable basis.
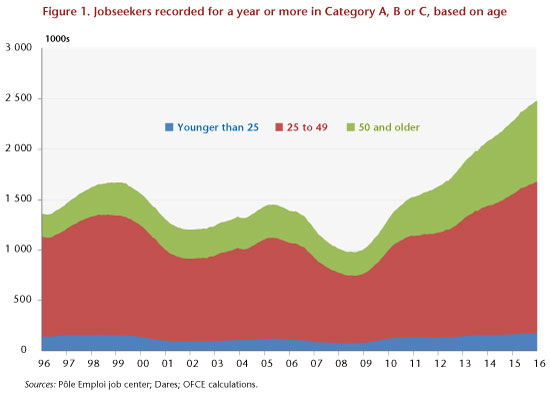
It is true that the increase in the numbers exiting the job centre due to regaining work (+ 5.1% over three months) is a positive sign, suggesting that the expected recovery is underway. Nevertheless, even though a pickup in employment has occurred, it has not been strong enough to halt the steady rise in the number of long-term unemployed (+9.1% in one year). Thus, in a context of near-zero average growth since 2008 and a continuing deterioration in the labour market, the share of the unemployed registered for a year or more in categories A, B or C has increased since mid-2009 (by 31% approximately) and is now at a historical high, representing 45.4% of all jobseekers in categories A, B or C (Figure 1).
This increase is explained by the rise in unemployment among older workers (+ 8.9% yoy): the implementation of a series of pension reforms (2003, 2010), coupled with the elimination of job search waivers for seniors, has led to prolonging the working life and to a later retirement age. In a context of weak growth, the increase in the employment rate of older workers has been insufficient to absorb the growth in the working population in this age group, with a consequent rise in unemployment among those over age 50 (see La suppression de la Dispense de recherche d’emploi: quand les gouvernements augmentent volontairement le décompte des chômeurs ! [The elimination of job search waivers: when governments voluntarily increase the unemployment count – in French].
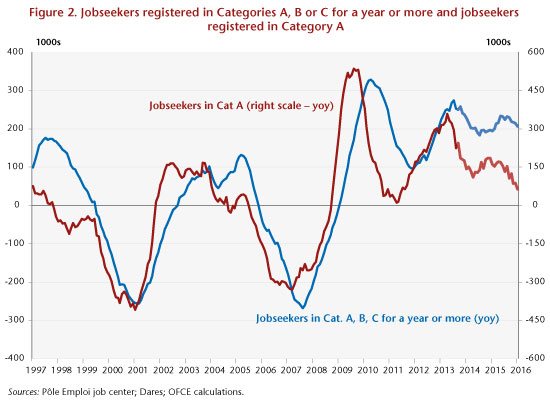
The relative improvement in the labour market expected in the coming months would stem from a slight improvement in growth and from the implementation of a training plan for the unemployed, announced by President François Hollande in late December 2015. However, it will take a long time for this improvement to affect the long-term unemployed. Indeed, the time taken for a fall in the numbers of Category A jobless to be transmitted to the long-term unemployed is relatively long (Figure 2). In the late 2000s, a period that saw a significant drop in jobless numbers, it took almost a year and a half for the fall in Category A jobless to result in a significant drop in the number of the long-term unemployed. The mechanisms for a pickup in jobs are clearly subject to considerable inertia.
[1] Because of this change in methodology, the unemployed have had one day less to complete their updates, leading in practice to a significant increase in the number of those struck off due to a failure to update (+1.5% in three months).