The end of a cycle?
OFCE Analysis and Forecasting Department
This text is based on the 2018-2019 outlook for the world economy and the euro zone, a full version of which is available here [in French].
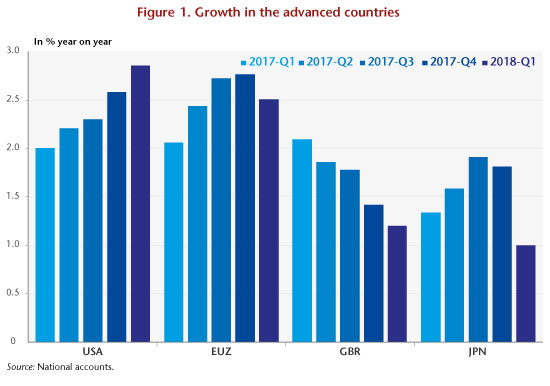
Global growth remained buoyant in 2017, allowing both the recovery and the reduction in unemployment to continue, especially in the advanced countries where growth rose to 2.3%, up from 1.6% the previous year. Although there are still a few countries where GDP has not recovered to its pre-crisis level, this improvement will gradually erase the stigma of the Great Recession that hit the economy 10 years ago. Above all, activity seemed to be gathering pace at the end of the year as, with the exception of the United Kingdom, annual GDP growth continued to pick up pace (Figure 1). However, the gradual return of the unemployment rate to its pre-crisis level and the closing of growth differentials, particularly in the United States and Germany, which had widened during the crisis, could foreshadow a coming collapse of growth. The first available estimates of growth in the first quarter of 2018 seem to lend credence to this assumption.
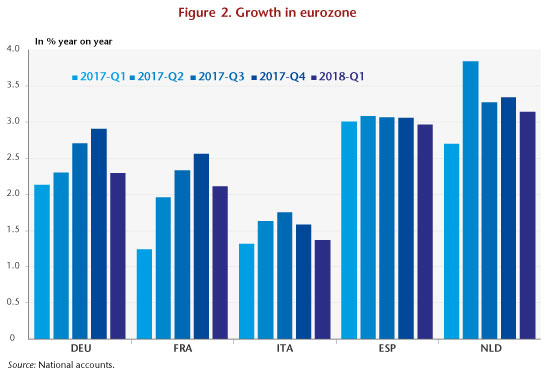
After a period of improvement, euro zone growth stalled in the first quarter of 2018, falling from 2.8% year-on-year in the fourth quarter of 2017 to 2.5%. While the slowdown has been more significant in Germany and France, it can also be seen in Italy, the Netherlands and, to a lesser extent, Spain (Figure 2). As for the United Kingdom, the slowdown is continuing as the prospect of Brexit draws nearer, while the country’s budgetary policy is also more restrictive than in the other European countries. Japan is experiencing rather more than a slowdown, with quarterly GDP growth even falling in the first quarter. Finally, among the main advanced economic countries, growth is still gathering steam only in the United States, where GDP rose 2.9% year-on-year in the first quarter of 2018.
Does the slowdown testify to the end of the growth cycle? Indeed, the gradual closing of the gaps between potential GDP and actual GDP would steadily lead countries towards their long-term growth paths, with estimates converging at what is indicated to be a lower level. In this respect, Germany and the United States would be representative of this situation since the unemployment rate in the two countries is below its pre-crisis level. In these conditions, their growth would be slowed. It is clear that this has not been the case in the United States. We must therefore refrain from any generalized conclusion. In fact, despite the fall in unemployment, other indicators – the employment rate – provide a more nuanced diagnosis of the improvement in the state of the labour market in the US. Furthermore, in the case of France this performance is mainly the consequence of the fiscal calendar, which caused a decrease in household purchasing power in the first quarter and therefore a slowdown in consumption [1]. This would therefore amount more to an air pocket than the sign of a lasting slowdown in French growth.
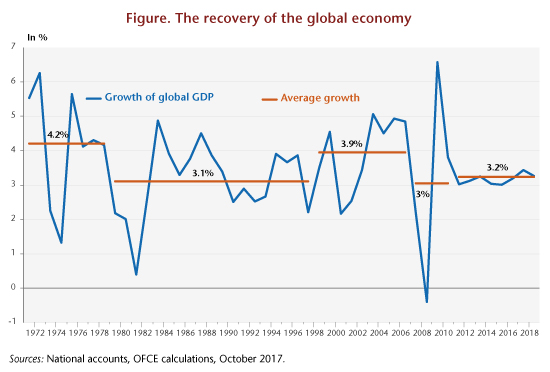
Above all, the factors that have supported growth will not generally be reversed. Monetary policy will remain expansionary even if a normalization is already underway in the United States, with the euro zone to start in 2019. On the fiscal side, the focus is more often neutral and should become highly expansionary for the United States, pushing growth above its potential. Finally, there are many uncertainties about estimates of the growth gap, meaning that maneuvering room might not necessarily be exhausted in the short term. An economic recovery is in fact still not being accompanied by a return of inflationary pressures or sharp wage increases, which would then indicate that the labour market is overheating. We anticipate continued growth in the industrialized countries in 2018 and accelerating growth in the emerging countries, bringing global growth to 3.7% in 2018. Growth should then peak, slowing down very slightly in 2019 to 3.5%. In the short term, the growth cycle would not then be over.